Published Apr 2024
An Overview of Vietnam
With one of the fastest growing economies in S E Asia, Vietnam benefits from its status as an attractive foreign investment opportunity, with a well-developed manufacturing infrastructure, a strong telecommunications industry and an educated workforce.

General:
With one of the fastest growing economies in S E Asia, Vietnam benefits from its status as an attractive foreign investment opportunity, with a well-developed manufacturing infrastructure, a strong telecommunications industry and an educated workforce.
Vietnam’s largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (formerly Saigon), known colloquially as HCMC. Considered the financial hub of Vietnam, HCMC is now making a name for itself as one of the fastest growing cities in Asia and recently made it to ninth on the list of global cities for High Net Worth Individuals, with particularly rapid growth in financial services, telecoms, technology and electronics. In 2023 HCMC had a total registered capital of over 5.85 billion USD, making up 16% of the countries’ total and increasing 48.5% from the previous year.
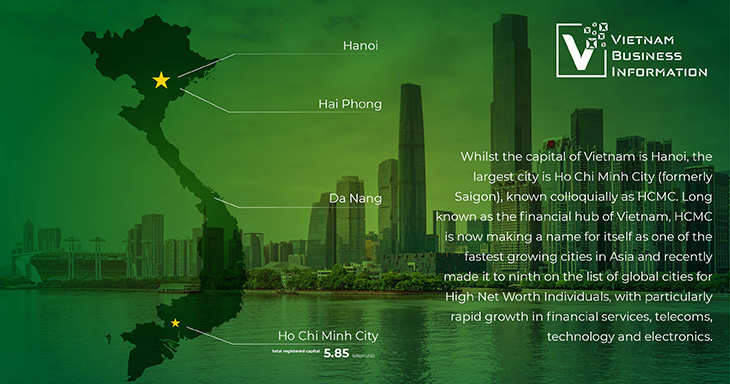
Hanoi is Vietnam’s capital and cultural hub, home to most of Vietnam’s government buildings. It boasts lower labor costs than HCMC and is an ideal location for domestic and international business. Tourism, both in Hanoi and the surrounding provinces, is a strong emergent sector and Hanoi has unparalleled access to the Red River Delta’s manufacturing, agricultural and technology industries.
Haiphong is Vietnam’s third largest city and is also known for its seaport, which offers a convenient path for imports and exports into the greater Hanoi metropolitan area. Da Nang benefits from a central location, a rapidly improving infrastructure and a high score on the quality of life index that attracts many well-qualified Vietnamese locals, coupled with an innovative approach to start-ups.
In 2023, capital generated by Foreign Direct Investment projects throughout the Vietnamese economy was estimated at 23.18 billion USD, up 3.5% over the same period in 2022. The accumulated realised capital of foreign investment projects reached about 297.2 billion USD, equalling 63.4% of the total valid registered investment capital.* In 2022, Vietnam’s GDP grew by 8.02%, outperforming government targets of 6.5% as well as global and regional growth projections and is expected to do so again in 2023.
Currency
Vietnam’s currency is the dong, issued by the State Bank of Vietnam and considered one of the more stable Asian currencies. Pegged to the value of the US dollar, the exchange rate stability has aided Vietnam in attracting foreign business investment.
Language
Vietnamese is the official language, with English spoken by many Vietnamese people, particularly in the main cities. Older Vietnamese citizens may also speak French and/or Russian. However, some Vietnamese don’t understand English, especially in remote areas, so it’s recommended that you consider if your business will need a translator or interpreter for your visit. Interpreters will also be able to guide and advise you regarding Vietnamese cultural norms.
Telecommunications
SIM cards are available everywhere, including at all airports, and your passport must be shown when purchasing one. As a visitor to Vietnam, it is important that you register your SIM card with an approved provider: the recommended company is Viettel, the largest telecoms provider in Vietnam and owned by the Vietnamese government.

In Vietnam mobile data is very cheap, with a month of unlimited 4G data (max. 2GB per day) costing less than 5 USD.
Find a Supplier for Your Business
International businesses are well-catered for when it comes to locating resources and researching potential Vietnamese suppliers and partners: the Vietnamese embassy, the Trade Commission and the Vietnamese Trade Promotion Agency all have dedicated departments for international business promotion that can contribute to market / sector data and analysis. In addition, there are on-the-ground agents, trade magazines, trade associations and many online companies offering a well-informed scrutiny of the Vietnamese economy.
Traveling to Vietnam
Most foreign citizens must have a visa when visiting Vietnam. Visa applications can be made in advance from a Vietnamese embassy, online through the Immigration Department website (E-Visa) or by obtaining a written letter of approval from a travel agency.
E-visas are popular and simple to purchase, costing 25 USD for a 30-day single entry visa and 50 USD for a 30-day multiple entry visa.
Internet
Wifi hotspots in Vietnam are easy to find, especially in major cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. Cafés, fast food restaurants, all hotels and office buildings can provide wifi.
Internet censorship is an issue in Vietnam: despite Vietnam’s economic reforms and openness to social change, including LGBT rights, media censorship is still strictly enforced by Vietnam’s Communist Party.
Vietnam Business Information


