Published Jan 2024
Positive outlook for Vietnam’s banking in 2024
Economic recovery, increased credit demand, reduced systemic risk, bottomed NIM and more positive profit outlook are expected to be factors that will help the banking system of Vietnam have a strong start in 2024.

In its 2024 outlook report, Mirae Asset Vietnam Securities (MASVN) pointed out a series of signs that the banking industry will prosper in 2024.
Recovery in credit
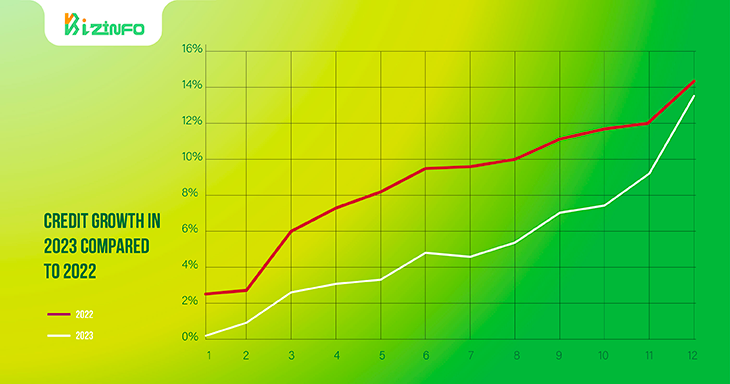
Analysts assess that high credit growth in the fourth quarter of 2023 may not be immediately converted into the bank's 2023 profits. However, late disbursement will contribute to 2024 profits.
MASVN forecasts that corporate lending will continue to be the driving force for credit in the last quarter of 2023. By 2024, credit segments will have more balanced growth.
The State Bank (SBV) announced the credit growth target for 2024 at 15% and allocated it to each bank very early.
Based on the expectation that macroeconomic conditions will improve both domestically and internationally in 2024, MASVN believes that the above credit growth target is feasible and does not carry too many risks in the future.
Reduced risks
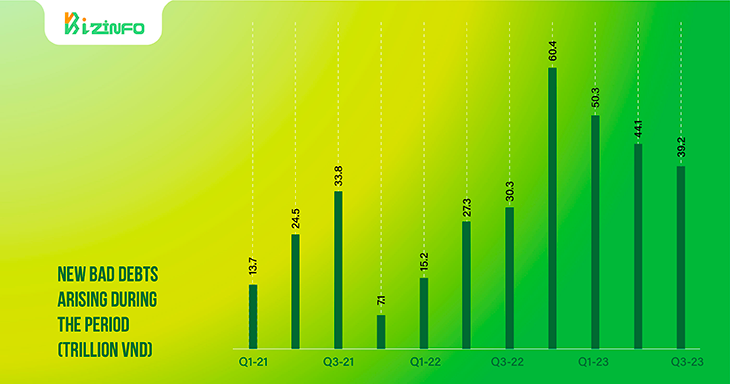
According to MASVN's assessment, despite the continuous increase in the bad debt ratio, some indicators show that this ratio will soon peak. Factors supporting the above forecast include: continuously lowering interest rates, economic recovery, and decreasing the rate of overdue debt formation.
Analysts believe that a decrease in lending interest rates, along with economic recovery, will slow down the rate of bad debt formation, while credit growth will limit the bad debt ratio. Furthermore, the above developments can help increase income, contributing to reducing the burden of provisions.
The gross bad debt ratio (including debt from groups 2 to 5) of listed banks is differentiated in the third quarter of 2023 but generally tends to improve. In addition, the rate of new bad debt formation has been continuously decreasing over the past 4 quarters.
MASVN believes that it is not too optimistic to believe that the bad debt ratio will soon peak in late 2023 or the first half of 2024.
While bad debt has increased, the loan loss reserves ratio (LLR) has decreased. Analysts forecast that with earnings expected to recover and bad debt rising slowly again, the LLR ratio could gradually improve in 2024.
In addition, from the end of 2022, a large amount of corporate bonds about to mature in 2023 and 2024 have raised concerns about systemic risk.
However, in 2023, everything was still under control. Experts say that this year, the amount of maturing bonds will be most concentrated in the fourth quarter when the economy is expected to gradually recover. MASVN concluded that in the short term, systemic risks still exist, but have been minimized to a certain extent.
CASA has recovered, NIM is about to bottom
According to MASVN, the continuous decrease in deposit interest rates has had a positive impact on the current account savings account (CASA) from around mid-2023. In general, an upward trend in CASA was recorded in the second and third quarters of 2023.
On average, the CASA of listed banks increased by 1.4 percentage points from a low in the first quarter of 2023 to 19.8% at the end of the third quarter of 2023. Analysts expect the CASA ratio to continue to recover in the coming quarters when deposit interest rates are less attractive, thereby reducing mobilization costs for banks.
At the same time, it is believed that net interest margin (NIM) is also showing signs of bottoming out. In the previous period, asset quality declined and mobilization costs increased sharply, putting pressure on NIM.
Specifically, the average NIM of listed banks decreased by 0.75 percentage points in the first 9 months of 2023, down to 3% at the end of the third quarter of 2023. However, the pace of NIM contraction of large banks is showing signs of slowing down, even increasing.
According to MASVN, the main assumptions for NIM recovery in 2024 include CASA having bottomed out, mobilization costs falling, and positive credit growth.
However, the level of recovery will be different for each bank, depending on the nature of the loan portfolio (customer group and lending sector) as well as the ability to optimize the term structure between assets and liabilities.
Source: MASVN
Compiled by VBI